Due to their complex and ever-changing nature, airport areas require particular attention in terms of air safety. Construction projects in the vicinity of airports must be approved by the civil aviation authorities, represented by bodies such as the Direction Générale de l’Aviation Civile (DGAC). These bodies may require EM impact studies to assess the risks of disruption to air navigation systems, notably radars and ILS, on runways and aircraft approaches.
Radar and ILS interference studies in airport zones
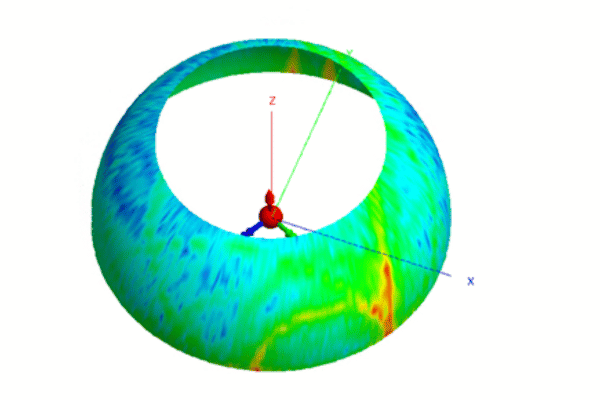
Airports and their surroundings are places of constant change and growth. Urban development, new building construction, infrastructure projects such as bridges, cranes and construction machinery can potentially create interference with air navigation systems, such as radars and instrument landing systems (ILS). Such interference represents a significant risk to flight safety, and requires careful assessment. In this article, we look at the methodologies and processes used to study these interferences, and the solutions for mitigating them.
1. Background and need for Electromagnetic Impact (EMI) studies
2. Methodology for Radar Interference Studies
2.1 3D building modeling
The first step is to create a precise three-dimensional model of the building or obstacle in question. This model takes into account the obstacle’s dimensions, shape and materials.
2.2 Positioning in the georeferenced reference frame
The modeled building is then positioned in a geo-referenced frame relative to the radar. This enables precise evaluation of distances and angles between the radar and the obstacle.
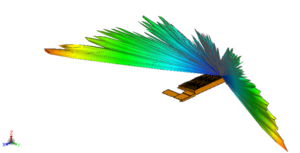
2.3 EM simulations
Electromagnetic simulations are carried out. These simulations assess the risk of radar glare (unwanted reflections), as well as the risk of multipath on runways and aircraft approach paths.
2.4 Processing EM results
Simulation results are analyzed using analytical formulas to assess the risk of false detections. We check whether emitted or reflected signals exceed primary or secondary radar thresholds, which could mislead operators as a result of phantom echo generation.

2.5 Risk mitigation recommendations
Based on the results obtained, recommendations are made concerning geometries, materials or locations to mitigate the risk of radar interference. These recommendations are designed to ensure flight safety and the reliability of air navigation systems.
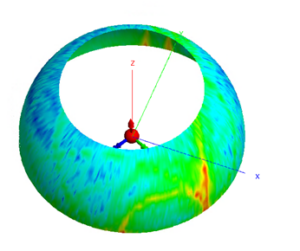
3. ILS studies and Obstacle Impact Analysis
The ILS is an instrumental guidance system used by pilots to help them land in poor visibility conditions. Obstacles in the vicinity of runways can interfere with the signals emitted by ILS systems, compromising the accuracy of descent and runway centreline indications.
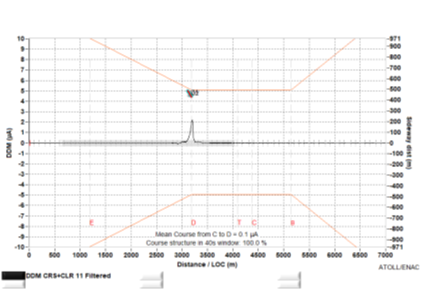
The software developed by the French Civil Aviation School (ENAC), Atoll/Lagon, is specially designed to assess the impact of obstacles on the DDM (Difference De Modulation) deviation of ILS systems. It can be used to check whether systems maintain runway categorization constraints in line with ICAO standards, despite the presence of surrounding obstacles.
4. Methodology for the ILS Study
4.1 Building modeling
The first step is to create an approximate but sufficient model of the building. This is represented by metal plates emulating the facades of the building to be constructed.

4.2 Positioning in the track marker
The modeled building is then positioned in a georeferenced reference frame in relation to the LOC or Glide, taking into account the thresholds and ends of the runway, its widths and key points.
4.3 EM PO simulations
Electromagnetic simulations based on the PO ray-tracing method are carried out. These simulations enable us to obtain an immediate result on the DDM and to conclude on the risk of the obstacle on the system.
Conclusion
Radar and ILS interference studies are essential tools for assessing the impact and optimizing construction projects in airport areas. By identifying and assessing risks at the earliest planning stages, these studies help avoid delays and costly complications, while guaranteeing the safety and efficiency of flight operations. By integrating these analyses into urban development processes, airport authorities and regulatory bodies help maintain high standards of safety and reliability in civil aviation.
A propos de l'auteur

Ingénieur spécialisé dans les modélisations et mesures radiofréquences et hyperfréquences depuis 2011.
Référent technique au sein du Bureau d’étude de Nexio.