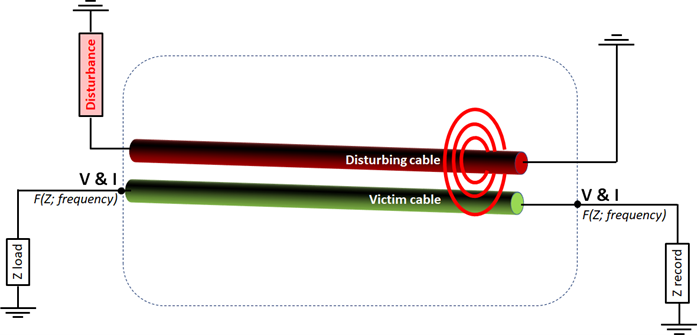
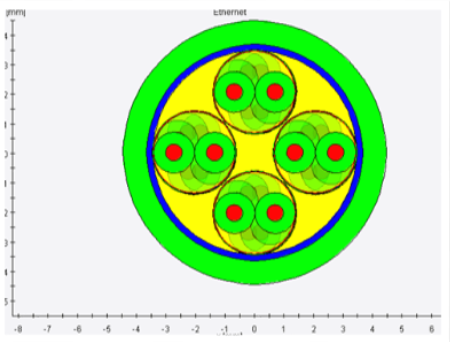
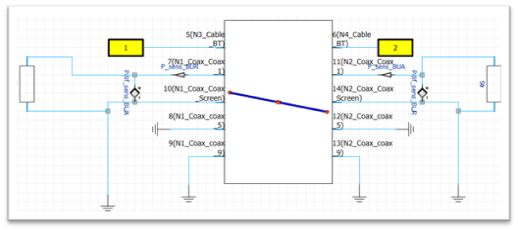
Crosstalk occurs when an electrical signal propagates along one conductor (called a disturbance cable) and induces an unwanted signal on an adjacent conductor (called a sensitive cable). This phenomenon is common in multi-conductor cables, and can lead to electromagnetic interference between the different conductors.
Numerical simulations aim to quantify the level of crosstalk between conductors, identify areas at risk of interference and explore ways of reducing crosstalk coupling, for example by altering the distance between conductors or using appropriate shielding techniques.