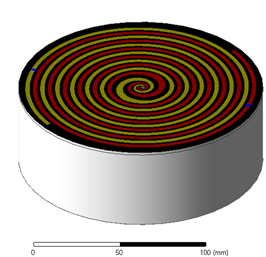
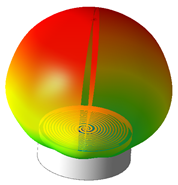
The model antenna is a double spiral with a diameter of 14.5 cm. The feed balun (not visible here) is integrated into the cavity. The cavity is designed to eliminate back radiation, which can be problematic for antenna integration.
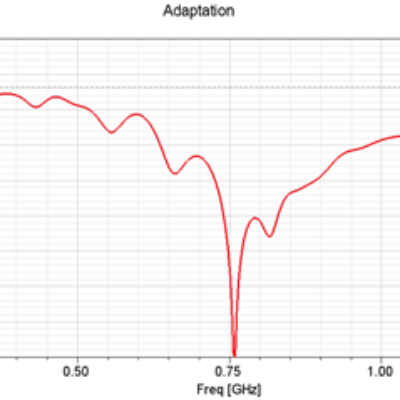
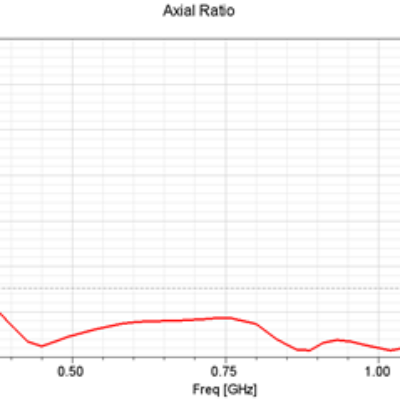
We study the antenna matching (figure 2) to find out its operating frequency range.